Top 10 Enterprise Technologies in 2009
Green IT
Green information technology (Green IT) is one of the fastest-growing initiatives in the industry. Green IT is rapidly moving from marketing and PR hype to reality in 2009 as manufacturers design, produce and distribute energy-efficient technology products. Green IT initiatives initially received recognition for the good intentions to reduce power consumption as an environmentally friendly initiative.

Green It is not just an earth friendly solution, but it is also a competitive technology for profitable business. Reduce costs are earned costs. Green IT enables the CIO to provide measured cost savings contributions to the company bottom line.
Recycle Accelerator
In keeping with the theme of earth friendly IT solutions, there has been a continuously growing awareness of the necessity for self-governance and producer responsibility when it comes to recycling excess and obsolete electronic and technology devices. The refurbishment and reuse of used computer equipment has enabled some global regions to enter the technology age at a rapid pace, acquiring the retired assets from other regions. This has created new problems for individuals and organizations as it pertains to protecting the private information stored on their drives.

Some products are the byproduct of tough love, unable to be salvaged or restored by refurbishing. These products may be recycled for materials. The materials may be used in future production. The goal of the last decade has been to minimize the amount of retired technology assets that end up in a landfill, mountain of trash, or a Sixty Minutes episode.
While the focus has been on proper handling, refurbishing, and resale of technology products, there is a significant shift of awareness that has taken place in 2008. Technology is now being developed and deployed to empower the very recyclers and recycling process that is intended to mitigate the trashing of technology products and encourage responsible actions.
Technology is being used to connect the constituents in the process, improve routing, and automate many of the manual processes for greater profit. The result is less hazardous waste, developing new business opportunities, and new revenue streams for the participants. Recycling initiatives offer ways to manage e-waste effectively; recycling solutions for obsolete mobile and wireless handhelds, personal computing devices, monitors, printers and ink cartridges.
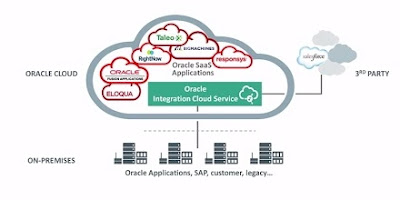
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is simply a buzzword used to repackage grid computing and utility computing, both of which have existed for decades. It is a style of computing in which massively scalable IT-related capabilities are provided as a service, using Internet technologies to support multiple external customers. Cloud computing offerings are often described in terms such as "on-demand services", "Hardware-as-a-Service (HaaS)", and "Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)".

Cloud computing is often used to sort through enormous amounts of data. In fact, Google has an initial edge in cloud computing precisely because of a need to produce instant, accurate results for millions of incoming search inquiries every day, parsing through the terabytes of Internet data cached on its servers. Microsoft Azure and Amazon's EC2 are the leading Clouds to be watched in 2009.
Next-Gen Virtualization
Virtualization technology received tremendous recognition and increasing adoption as a result of various economic benefits. Benefits include the need for fewer physical systems, lower energy costs, and less overhead management.

As businesses saw the first generation virtualization technologies value in 2008, the next generation of virtualization products and tools will enable businesses to realize the benefits of systems self-healing, self-managing, enterprise cloud computing, where applications are automatically guaranteed the right quality of service at the lowest operating cost by harnessing internal and external computing capacity.
Enterprise Web 2.0
Enterprise Web 2.0 describes the introduction and implementation of Web 2.0 technologies within the enterprise, including Rich Internet Applications (RIAs), Social Computing, Mash-ups, Software as a Service (SaaS), and using the web as a general platform.
Communications 2.0
Communication 2.0 is all about convergence of various communication and collaboration tools and platforms such as VoIP, VoWi-Fi, Wi-MAX, Web and Video Conferencing, Enterprise Social Computing, Presence, and IM Management. Communication 2.0 delivers cost effective internal communication and enables businesses to connect communities that encompass employees, customers, partners and others "outside the firewall". This empowers users to tap into both internal and external knowledge, and use that knowledge to accelerate innovation.
The technology will mature in 2009, forcing companies to look at all their collaboration points in a strategic way and tie them to business goals and processes. This new approach will transform them from toys to tools and will establish their place and value in the new order.
Storage
As the digitization of data continues to increase, the need for storage, de-duplication technologies have a primary role in helping enterprises manage the rampant growth of storage through the virtual infrastructure growth to meet the compliance and regulatory situations. We can expect products with the integration of Fibre Channel and Ethernet. Web 2.0 and Social networking will be the significant drivers of data storage and content security.

Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) promises to deliver exceptional flexibility and cost savings to IT by defining a methodology for the use and re-use of IT functions and business processes. Services are software components, constructed so that they can be easily linked with other software components at the enterprise level. The idea behind these services is to express the technology in dissected format that business people can understand rather than as an arcane application such as ERP or CRM.
SOA is focused on bridging the gap between business processes and IT through well defined, business-aligned services, developed along the established design principles, frameworks, patterns & methods. However, SOA is still at the early or pilot stage in several organizations, and businesses are still in the process of learning how to implement it so that it fulfills its potential for accomplishing desired business goals in the coming years.
Business Process Management (BPM)
The accelerated Legacy Modernization and IT infrastructure optimization processes will drive the BPM adoption faster in 2009. Businesses are looking for ways to improve the work and data flow so manpower resources can perform better, faster, and with less cost than the competition. Improved performance powers competitive differentiation. Business processes and rules management systems are designed to separate process and rules logically so they can be managed independently with agility.
Location Based Computing
The latest mobile and wireless handheld devices are powered with Global Positioning Systems (GPS). Location based applications can drastically improve the customer experience. GPS data availability will drive the creation and adoption of 'Location-Aware' business applications and enterprise mash-ups in 2009. Leaders in hardware include the iPhone, Blackberry, or Google Android, all with the ability to share location information and retrieve location specific data about local services, other people, events, sales, gas prices, and anything else that adds a new dimension to mobile applications and revenue growth opportunities.
Information Security
Web 2.0 technologies adoption by business paved new ways for the cyber criminals to attack the business network and applications in 2008. The exploitation of vulnerabilities in the database, poorly secured web apps, widgets and gadgets will be much greater in the foreseeable future. The use of sophisticated Trojan, keylogger, and rootkit crimeware that targets financial institutions and consumers will require better Information Security policies and products that can be constantly updated to keep pace with emerging threats. Information security concerns include identity theft, wiping data from retired hard drives, data access, and the risks of many networks.




Comments
Post a Comment